Tutorial¶
Let’s start using Qgis2threejs plugin!
Install the plugin¶
Open the Plugin Manager (Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins...) and
install Qgis2threejs plugin.
Hint
Need help? See the 9.1. Installing and Managing Plugins section of the QGIS training manual.
Obtain elevation data¶
If you already have raster DEM data, you can skip this step.
NASA published elevation data generated from NASA’s Shuttle Radar Topography Mission digital topographic data. We can use the data freely. SRTM elevation data can be downloaded from the EarthExplorer (User registration required).
✏
Load DEM data¶
✏
CRS setting¶
Horizontal unit of SRTM data is degree, whereas vertical unit is meter. For appropriate visualization, you need to transform the DEM data to a projected CRS. QGIS can perform the CRS transformation on the fly.
So, let’s change the current project CRS to a projected CRS.
Click the CRS status icon ![]() in the bottom-right corner of the window to
open the project properties dialog, and then select a suitable CRS for the DEM extent.
If you don’t know which CRS is best suited, select the Spherical Mercator projection
(
in the bottom-right corner of the window to
open the project properties dialog, and then select a suitable CRS for the DEM extent.
If you don’t know which CRS is best suited, select the Spherical Mercator projection
(EPSG:3857), which is adopted by many web maps.
Note
In the Spherical Mercator projection, every feature size is horizontally larger than actual size except those of features on the equator. At latitude 40 degrees it is enlarged 1.3 times, at 60 degrees enlarged twice.
Layer styling¶
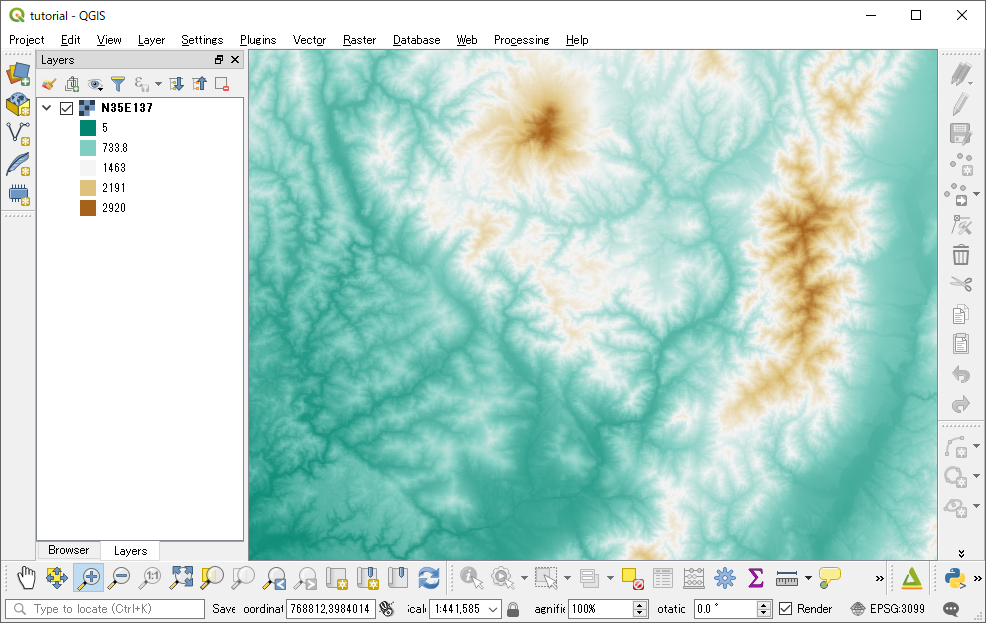
Open the Layer Properties dialog for the DEM layer and colorize the DEM layer richly.
An example (Singleband pseudocolor render type and inverted BrBG color map):
Open the Exporter¶
Zoom to a part of the DEM layer extent as the map canvas is filled by the colorized DEM layer,
and then click the plugin icon  in the web toolbar to open the Qgis2threejs exporter.
in the web toolbar to open the Qgis2threejs exporter.
There is Layers panel and Animation panel on the left side of the window.
The Layers panel shows the map layers in the current QGIS project that can be added to the 3D scene.
Layer items are grouped by type. DEM layer group has 1-band raster layers in current QGIS project and
a Flat Plane (a flat plane at an altitude). Multi-band raster layers and raster layers loaded using
a provider other than GDAL provider are not available. Additional flat planes can be added from
Scene - Add Layer menu.
There is a preview on the right side. The scene doesn’t contain any 3D objects now.
Let’s add the DEM layer into the scene. Just click the checkbox on the left of the DEM layer under the DEM layer group.
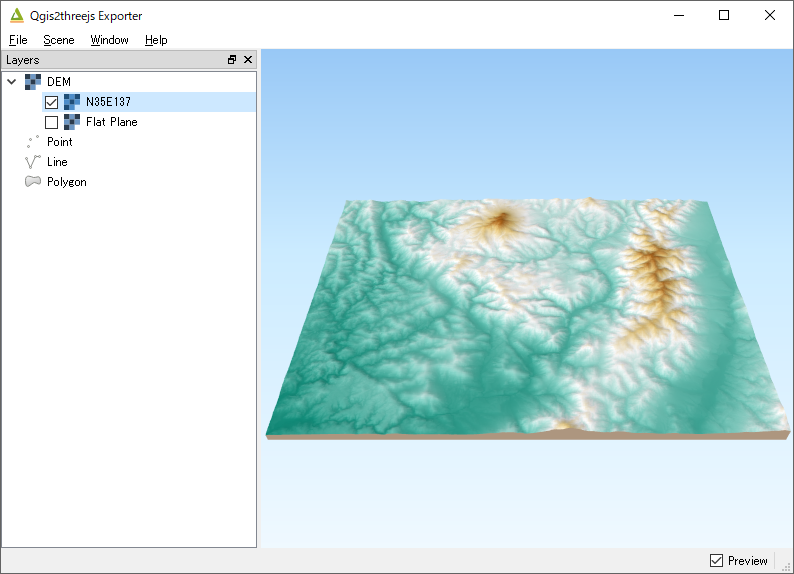
A 3D terrain object with map canvas image draped on it shows up in the preview.
Add another texture to DEM¶
✏
Export the scene to Web¶
Click on the File - Export to Web... menu entry to open this dialog.
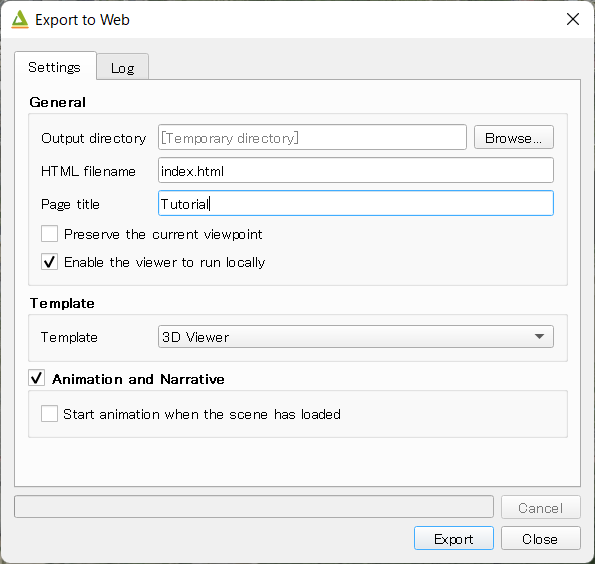
Select a directory to export the scene, check Enable the Viewer to Run Locally option and press Export button.
Note
Most web browsers do not allow loading data files on local file system via Ajax.
With Enable the Viewer to Run Locally option the plugin outputs geometry and image data into a js file.
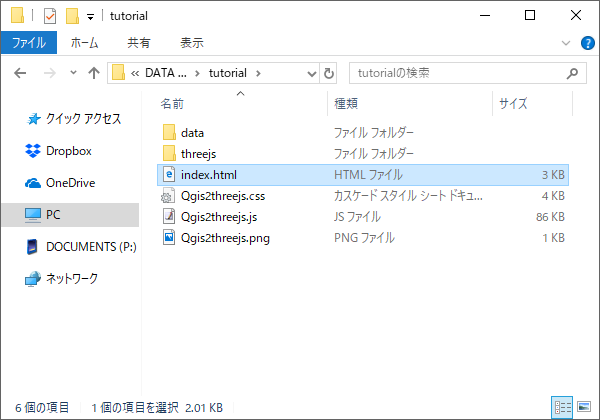
Open the .html file with a web browser. You can see exported scene in web browser.
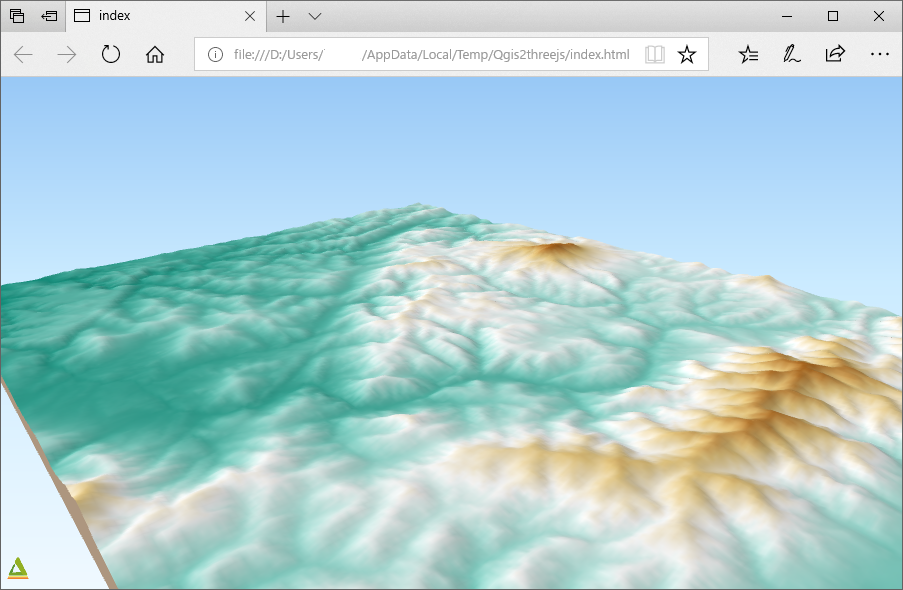
You can publish the exported 3D viewer application and data just by uploading the output folder to a web hosting service such as Netlify and GitHub Pages.
Note
Please do not forget to ensure that you comply with the Terms and use for the data before publishing the data to the web.
Animation and narratives¶
✏
In conclusion¶
Tutorial is over. Now you know 3D visualization with QGIS is very easy. If you can use high-quality data, you can create beautiful 3D scenes!
Tip
Next, how about adding a background map layer to the map canvas. You can do it easily with QuickMapServices plugin. Also, how about adding vector data to the scene. Object Types page has images of various object types. See Exporter for the detail.